What is Throttling Policy in Exchange 2016
In Exchange Server environment, there is a policy that has responsibility to regulate, control and manage the application rate and performance known as Throttling Policy. This policy is by default activated in Exchange 2007 & all above versions, and has enhanced in different versions of Exchange Server. There are some improvements which have been applied in each versions of Exchange server from 2007 to 2016 and all these improvement provides enhanced features to monitor & control the performance. In this blog, we are going to learn about what is throttling policy in Exchange server 2016.
About Throttling Policy in Exchange Server 2007
This policy was first introduced as a new feature in Exchange 2007 and was named as RPC Client Throttling. This feature allow administrators to control & manage the performance of end-users by preventing different client applications. Through this policy, a “back-off” request is sent to the client, whenever Exchange server find out some negative effect from any specific mailboxes. It notify users that sending of any requests should postponed for some specific period of time so that one can prevent the server from going into any hazardous situation, which may lead to decrease of exchange server performance.
The data of back-off request contains two parts which are described below:
- The first part comprises of the time when insertion of back-off take place.
- The second part includes the time period of back-off request. Moreover, this time period is calculated by the following formula:
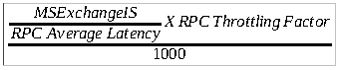
By default, the value of RPC throttling factor is 1000. The RPC Average Latency should be less than 100 milliseconds for maintaining the performance of the server. The back-off value of server to client will be in milliseconds, till the expiration of back-off request time period.
For Outlook 2007 users, a ropBackoff request is inserted to the back-off queue of user which involves the information related to current delay of back-off request, and notify its clients to postpone any additional server requests for certain time duration.
About Throttling Policy of Exchange Server 2010
In Exchange Server 2010, the throttling policy has became more advanced with improved feature of monitoring and controlling the performance of the server. Here, this policy is named as Client Throttling feature, which manages the performance of Client Access Server and measures the amount of resources utilized by users.
NOTE: There is an another Throttling policy in Exchange 2010 i.e. Message Throttling, which bounds the number of messages and connection processed by Exchange Transport Server. However, in this article, we are going to discuss about Client Throttling feature only.
Automatically, a default throttling policy is generated at the creation time of Exchange environment. Generally, this default policy is sufficient for managing the Client access server, but you can also alter the policies or add new sub-policies as per your requirement. The policies or sub-policies enabled by users are termed as non-default policy. The policy provides administrator a facility to fix an acceptable load on user-to-user basis.
The structure of throttling is designed in such a way that it defends the resources of Exchange server. Accidentally, if non-default policies gets corrupted or is missing, then the throttling policy will automatically fall back to its default structure. In addition, if a situation occurs in which default policy is corrupted, then throttling policy will fall back into the fallback policy of the Exchange because this policy is inbuilt in Exchange, therefore it is less likely to fail.
For altering or adding the throttling policies, one should have knowledge about the fact that the settings of the policy is modified through Exchange Management Shell by making use of some cmdlet commands of Exchange Management Shell and they are named below:
- Get-ThrottlingPolicy: For viewing settings of throttling policy
- Set-ThrottlingPolicy: For modifying the current settings of throttling policy
- New-ThrottlingPolicy: For creating a new throttling policy
- Remove-ThrottlingPolicy: For removing an existing throttling policy
There are some parameters available in Windows PowerShell and they are discussed below:
- PowerShellMaxConcurrency: This parameter defines the highest number of a remote session, which Shell user can open it. It also determines the occurrence number of cmdlets that remote Shell users are executing.
- PowerShellMaxCmdlets: This is a dependent parameter that determines number of times a cmdlet can be executed within a time period, without being limited. However, this parameter is fully dependent upon the value of another parameter i.e. PowerShellMaxCmdletsTimePeriod.
- PowerShellMaxCmdletsTimePeriod: Another dependent parameter that defines the time period in which a Shell user can execute cmdlets that is determined by PowerShellMaxCmdlets. The time period is defined in seconds.
- PowerShellMaxCmdletQueueDepth: Through this parameter, one can determine the number of operations, which a user can perform, simultaneously. However, this parameter affects the working of two cmdlets i.e. PowerShellMaxCmdlets and PowerShellMaxConcurrency.
Due to use of throttling policies, there may occur two major issues in Exchange 2010. The first major issue is inadequate BES policy and the other is due to synchronization problem with mobile devices. Throttling policy supports connection of up-to 10 mobile devices at one time. Therefore, a trouble may arise if users connects more than 10 mobile devices. In addition, for connecting more than 10 devices users can modify the default settings of throttling policy.
About Throttling Policy in Exchange 2013
In Exchange Server 2013, the feature named as Exchange Workload provides the same functioning as of Throttling Policy in Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010. It manages the system resources of Exchange server by consuming system resources like Active Directory, CPU, etc. Controlling and managing the system resources of Exchange server was possible in Exchange Server 2010, but this facility is being expanded in Exchange server 2013. The policy makes sure that resource consumed by each user does not affect the performance of server and provide users a trouble-free working on server. The enhanced feature enables users to use more and more resources within short duration and without bandwidth reduction.
There exist a default throttling policy in Exchange 2013 and this default policy is known as GlobalThrottlingPolicy because scope of this default policy is Global in this server. There are other scopes available for users i.e. Organization and Regular. But here we will learn only about policy having Global scope. For new and existing user of any organization who are using Exchange Server 2013 environment, the GlobalThrottlingPolicy determines the baseline of default throttling settings.
The developers of Exchange 2013 strongly recommend its users that they should not alter the default settings of throttling policy. However, one can create an additional throttling policy for managing their own workloads. If one is using Organization scope, then users can customize throttling settings according to their organizational needs by creating a new throttling policy with Regular scope. While creating a new policy, set the throttling settings in such a way that they are different from GlobalThrottlingPolicy or any other policies.
Similar to Exchange 2010, there are four cmdlet commands for system resources management using Exchange Management Shell. These cmdlets are same as in Exchange 2010, providing the same functioning.
I have not written anything about throttling policy in Exchange 2016, because there is not any improvement in throttling policy over exchange 2013 throttling policy. There is completely same throttling policies are being used in Exchange Server 2016.
Observational Verdict
In this article we have discussed about what is throttling policy in exchange 2016. We discussed about throttling policy from beginning since it had started to come as a default functionality with exchange 2007. With change of time and exchange server throttling policy also improved its feature. But if we talk about improvement of throttling policy of exchange server 2016 in comparison with exchange 2013 then there is not any improvement yet. But Microsoft might introduce some changes in throttling policy as an update feature of exchange server 2016.
Along with the development in technologies, there has been a great improvement in the throttling policies of Exchange server. The improvement of Client Throttling Policies in different versions of Exchange is a part of commitment given by Microsoft for upgrading the performance of Exchange & providing administrators with more advance features to control end-users.